Press Release on the first Q3D Paper
Link to the ESA and NASA press releases of the first results from the JWST Q3D Project.
Learn moreFeedback from accreting supermassive black holes is now a standard ingredient in galaxy formation models. It is seen as necessary for explaining the steep decline of the galaxy mass function and for establishing the black hole vs. bulge correlations. In the last few years, optical and near-IR integral field unit (IFU) observations have provided new physical insights on this important issue. While these ground-based observations are limited by the Earth’s atmosphere, they provide tantalizing hints at the coming revolution that JWST’s high-resolution, near- and mid-IR capabilities will bring to this area of research. JWST will revolutionize our understanding of black hole-galaxy co-evolution by allowing us to probe the stellar, gas, and dust components of nearby and distant galaxies, spatially and spectrally. The JWST ERS Program "Q3D" makes use of the IFU capabilities of NIRSpec and MIRI and will study the impact of three carefully selected luminous quasars on their hosts. Our program will provide a scientific dataset of broad interest that will serve as a pathfinder for JWST science investigations in IFU mode. Luminous quasars are also excellent test cases for the PSF decomposition and spectral analysis package q3dfit that our team will provide for the community. For a wide range of extragalactic phenomena (e.g. quasars, starbursts, supernovae, gamma ray bursts, tidal disruption events) and beyond (e.g. nebulae, debris disks around bright stars), PSF contamination will be an issue when studying the underlying extended emission and our new data analysis tool that will enable frontier science for a wide swath of astrophysical research.
PI: Dominika Wylezalek University of Heidelberg, GER
Co-PI: Sylvain Veilleux University of Maryland, College Park, USA
Co-PI: Nadia Zakamska Johns Hopkins University, USA
Software Lead: Dave Rupke Rhodes College, USA
Caroline Bertemes University of Heidelberg, GER
Andrei Vayner Johns Hopkins University, USA
Yuzo Ishikawa Johns Hopkins University, USA
Weizhe Liu University of Maryland, College Park, USA
Jorge Barrera-Ballesteros UNAM, Mexico
Nora Luetzgendorf Space Telescope Science Institute/ESA, USA
Nicole Nesvadba Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale, France
Hsiao-Wen Chen University of Chicago, USA
Macarena Garcia Marin Space Telescope Science Institute/ESA, USA
Jenny Greene Princeton University, USA
Kevin Hainline University of Arizona, USA
Fred Hamann University of California, Riverside (USA)
Tim Heckman Johns Hopkins University, USA
Sean Johnson Princeton University, USA
Guilin Liu Univ. of Science and Technology (China)
Dieter Lutz Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, Germany
Vincenzo Mainieri European Southern Observatory, Germany
Roberto Maiolino Cambridge University, UK
Patrick Ogle Space Telescope Science Institute, USA
Eckhardt Sturm Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, Germany

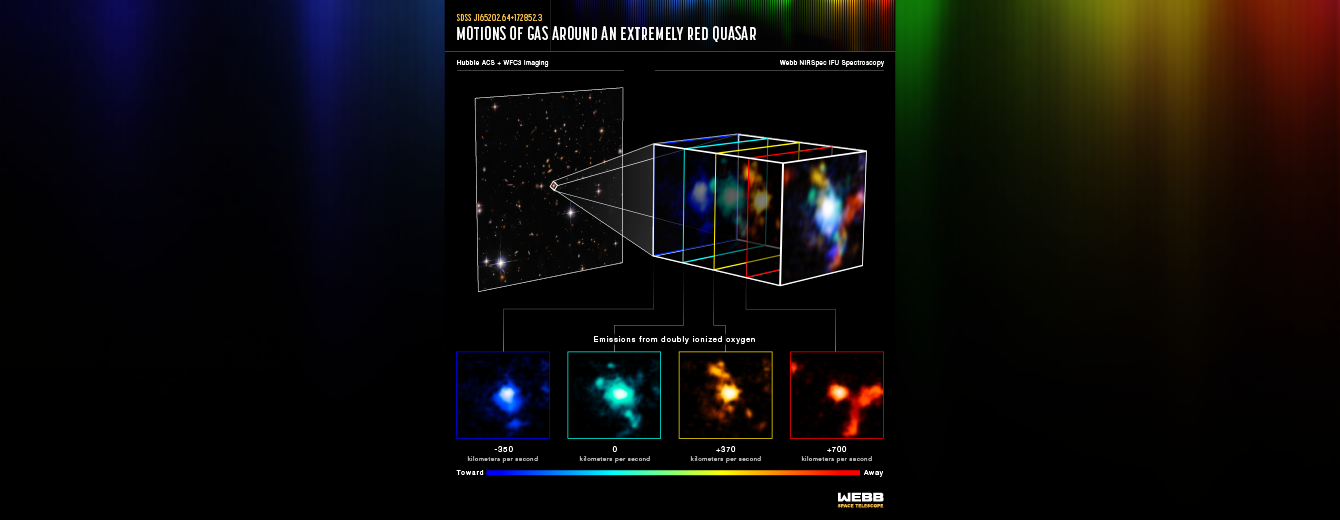
"First results from the JWST Early Release Science Program Q3D: The Warm Ionized Gas Outflow in z ~ 1.6 Quasar XID 2028 and its Impact on the Host Galaxy", Sylvain Veilleux, Weizhe Liu, Andrey Vayner, Dominika Wylezalek, David S. N. Rupke, Nadia L. Zakamska, ApJ submitted Link to the paper
"First results from the JWST Early Release Science Program Q3D: Ionization cone, clumpy star formation and shocks in a z=3 extremely red quasar host", Vayner, Andrey; Zakamska, Nadia L.; Ishikawa, Yuzo; Sankar, Swetha; Wylezalek, Dominika; Rupke, David S. N.; Veilleux, Sylvain; ApJ submitted Link to the paper
The first JWST paper is out!
"First results from the JWST Early Release Science Program Q3D: Turbulent times in the life of a z ∼ 3 extremely red quasar revealed by NIRSpec IFU", Wylezalek D., Vayner A., Rupke D.S.N. et al. ApJ, 2022 Link to the paper and press release.

q3dfit is custom software for scientific analysis of integral field unit (IFU) spectroscopy of quasars and their host galaxies, specifically aimed at producing science-ready measurements from James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) IFU spectrographs. q3dfit takes advantage of the spectral differences between quasars and their host galaxies for maximal-contrast subtraction of the quasar point-spread function (PSF) to reveal and characterize the faint extended emission of the host galaxy. Host galaxy emission is carefully fit with a combination of stellar continuum, emission and absorption of dust and ices, and ionic and molecular emission lines. q3dfit has been tested on ground-based data where PSF is weakly wavelength-dependent. The update of q3dfit to the case of the strongly wavelength-dependent JWST PSF is currently in development.
q3dfit Documentation and Download
Link to the ESA and NASA press releases of the first results from the JWST Q3D Project.
Learn more
A German TV team visited Dominika Wylezalek in Heidelberg to learn about JWST and Q3D.
Learn more
A summary of Q3D's aims and goals.
Link to the Article
Program Summary hosted on STScI Websites.
Learn more